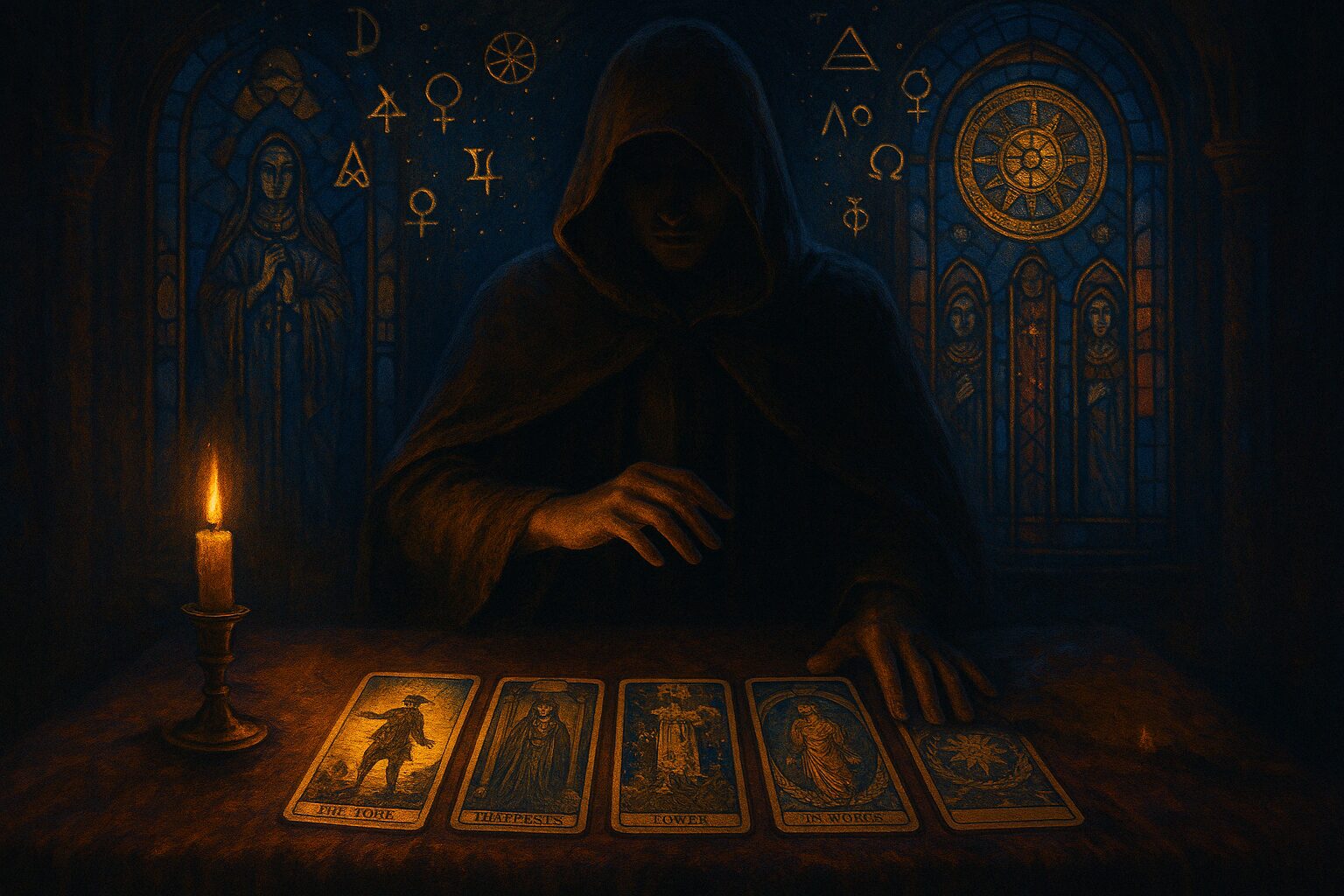
Introduction
Scrying—the art of seeing visions or gaining insights through the use of reflective surfaces—has captivated mystics and diviners for centuries. One of the most intriguing and powerful tools for scrying is the black mirror, a dark, reflective surface used to access hidden truths, spiritual guidance, and glimpses into the future. This article explores the historical and occult significance of the black mirror, its connection to the dark arts, and the ways in which it has been used in various traditions for divination and self-discovery.
The Origins of the Black Mirror
The use of reflective surfaces for divination can be traced back to ancient cultures, with early examples of scrying found in the rituals of the Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians. However, the black mirror specifically has roots in European occult traditions, where it was often associated with the darker, more mystical aspects of the occult.
The black mirror was historically used by witches, magicians, and mystics to:
- Peer into hidden realms
- Summon spirits
- Receive divine messages
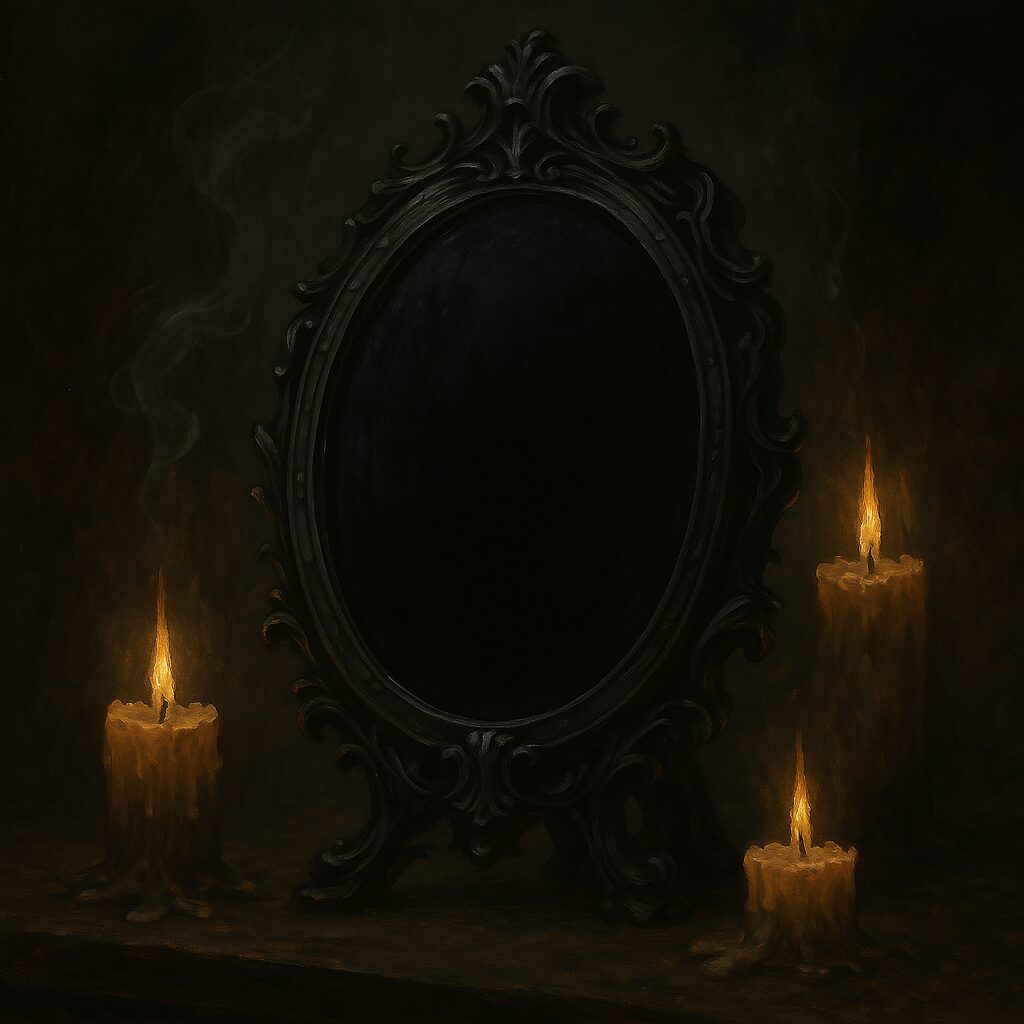
Unlike the traditional crystal ball, which is typically clear and allows for easy visibility of the inner visions, the black mirror’s opaque surface is said to invoke a more mysterious and complex interaction. The darkness of the mirror reflects the “dark” or unconscious aspects of the self, offering access to the shadow—those hidden parts of the psyche that often hold the key to profound spiritual revelations.
The Symbolism of Darkness: The Mirror as the Gateway to the Unconscious
In many mystical traditions, darkness is not seen as purely negative but as a symbol of potential and hidden wisdom. The black mirror serves as a portal to the unconscious mind, a place where one can encounter not only external forces but also the inner workings of the psyche.
Carl Jung on Shadow Work
Carl Jung, the renowned psychoanalyst, often discussed the importance of shadow work, which involves confronting the repressed or ignored aspects of the self in order to achieve integration and wholeness. The black mirror is a tool for shadow work, revealing the inner demons, desires, and hidden truths that, once acknowledged, lead to greater self-awareness.
In the occult text The Book of the Law, Aleister Crowley writes:
“The first step toward knowledge is the conquest of ignorance; it is achieved through knowing oneself.”
The black mirror, in this sense, functions as a mirror to the soul, reflecting not just the exterior but the deeper, unconscious parts that lie dormant within. By gazing into the darkness, one confronts the shadow and initiates the process of self-transformation.
The Art of Scrying with the Black Mirror
Scrying with the black mirror involves entering a state of deep concentration and meditation, allowing the practitioner to focus their attention on the dark surface. The process typically begins with the creation of a sacred space, free from distractions, where the scryer can focus fully on the mirror. The practitioner may light candles or incense to enhance the ritual atmosphere, creating a sense of spiritual reverence and openness.
Steps for Scrying:
- Create a Sacred Space: Ensure the area is free from distractions. Lighting candles or incense can help set a spiritual tone.
- Gaze into the Mirror: The practitioner enters a relaxed, meditative state, allowing their mind to enter an altered state of consciousness.
- Interpret Visions: As they focus on the black surface, images, symbols, or visions may begin to form. These are often metaphysical representations of hidden truths, future events, or spiritual messages.
In the tradition of Western occultism, the black mirror is believed to connect the practitioner with spiritual beings, including:
- Angels
- Ancestors
- Otherworldly entities
Some practitioners even use the black mirror for necromancy, attempting to contact the dead and receive their guidance or wisdom.
The Black Mirror in Historical and Occult Contexts
The black mirror has a long and varied history in the occult. It was used by practitioners of magic, witches, and fortune tellers throughout the medieval and Renaissance periods. One famous historical figure known for using the black mirror was John Dee, the infamous occultist and astrologer who served as an advisor to Queen Elizabeth I. Dee is said to have used a black obsidian mirror to communicate with angels and seek divine knowledge. He referred to this tool as a “shew-stone” and used it in his scrying rituals.
In more recent occult traditions, the black mirror has become a staple of modern divination practices. It is commonly used by contemporary witches, occultists, and spiritual seekers who wish to tap into the deeper, often unconscious realms of existence. The mirror’s dark surface invites a more introspective approach to divination, encouraging a process of inner exploration that is both personal and mystical.
The Psychological Aspects of Scrying
The psychological impact of scrying with the black mirror is profound, as it serves as a tool for introspection and self-exploration. The dark surface symbolizes the unknown aspects of the psyche—those repressed desires, fears, and memories that are often difficult to confront.
The black mirror offers an opportunity for psychological healing and growth. As Carl Jung famously said:
“One does not become enlightened by imagining figures of light, but by making the darkness conscious.”
As the scryer gazes into the mirror, they may experience a release of unconscious material, which can be both cathartic and transformative. Through this practice, the practitioner may encounter their shadow self and begin to integrate those aspects of the psyche that have been denied or ignored. This confrontation with the shadow is a vital part of the journey toward self-awareness and spiritual wholeness.
Conclusion
The black mirror is a powerful tool in the occult tradition, offering a direct pathway to the unseen realms and the deeper aspects of the self. Through scrying, the practitioner can:
- Unlock hidden knowledge
- Communicate with spiritual entities
- Engage in profound self-exploration
The mirror serves as a reflective surface not just for the material world but for the unconscious mind, revealing the darkness within and offering the possibility of transformation.
In the dark surface of the mirror, there lies not just an image of what is, but what could be—an invitation to delve into the depths of the unknown, confront the shadow, and emerge enlightened.
As the occultist and philosopher Aleister Crowley once wrote:
“The mind is the key to the universe, and the universe is infinite in its mystery.”
The black mirror, in all its dark allure, is one of the gateways to that infinite mystery.